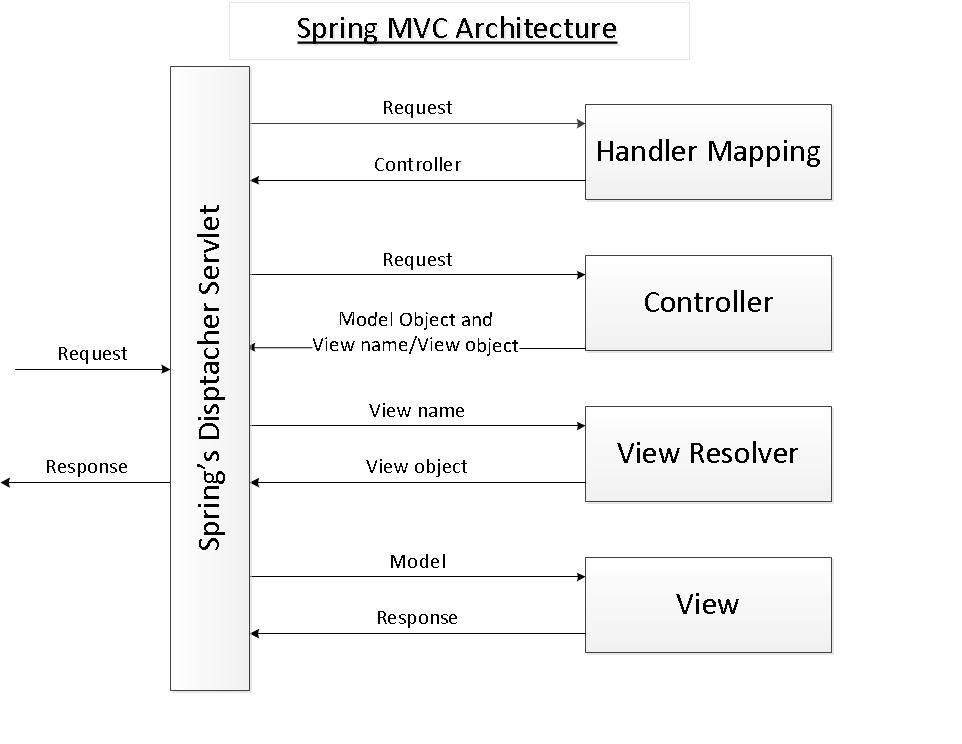
When sending a request to your application the following happens:
- The request arrives at your server (e.g. Tomcat). Depending on the context path in the url the server decides to which application the request belongs.
- Depending on the url and the servlet mapping in the web.xml file of your application the server knows which servlet should handle the request.
- The request is passed to the servlet filter chain which can modify or reject requests
- The servlet takes control over the request. In case of your Spring application the spring Dispatcherservlet receives the request. Now Spring kicks in
- The request is processed by mvc intercepters
preHandlemethods - The request is mapped to a controller based on the url. The corresponding controller method will be called.
- Your controller is processing the request. Many different responses can be returned in controllers (jsp, pdf, json, redirects, etc.). For now i assume you want to render a simple jsp view. Result of the controller are two things: a model and a view. The model is a map that contains the data you want to access later in your view. The view at this stage is most of the time a simple string containing a view name.
- Registered springs mvc interceptors can kick in again using the
postHandlemethod (e.g. for modifying the model) - The 'view' result of your controller is resolved to a real View using a
ViewResolver. Depending on the ViewResolver the result can be jsp page, a tiles view, a thymeleaf template or many other 'Views'. In your case theViewResolverresolves a view name (e.g. 'myPage') to a jsp file (e.g./WEB-INF/jsp/myPage.jsp) - The view is rendered using the model data returned by your controller
- The response with the rendered view will be passed to mvc interceptors again (
afterCompletionmethod) - The response leaves the dispatcher servlet. Here ends spring land.
- The response passes servlet filters again
- The response is send back to client
No comments:
Post a Comment